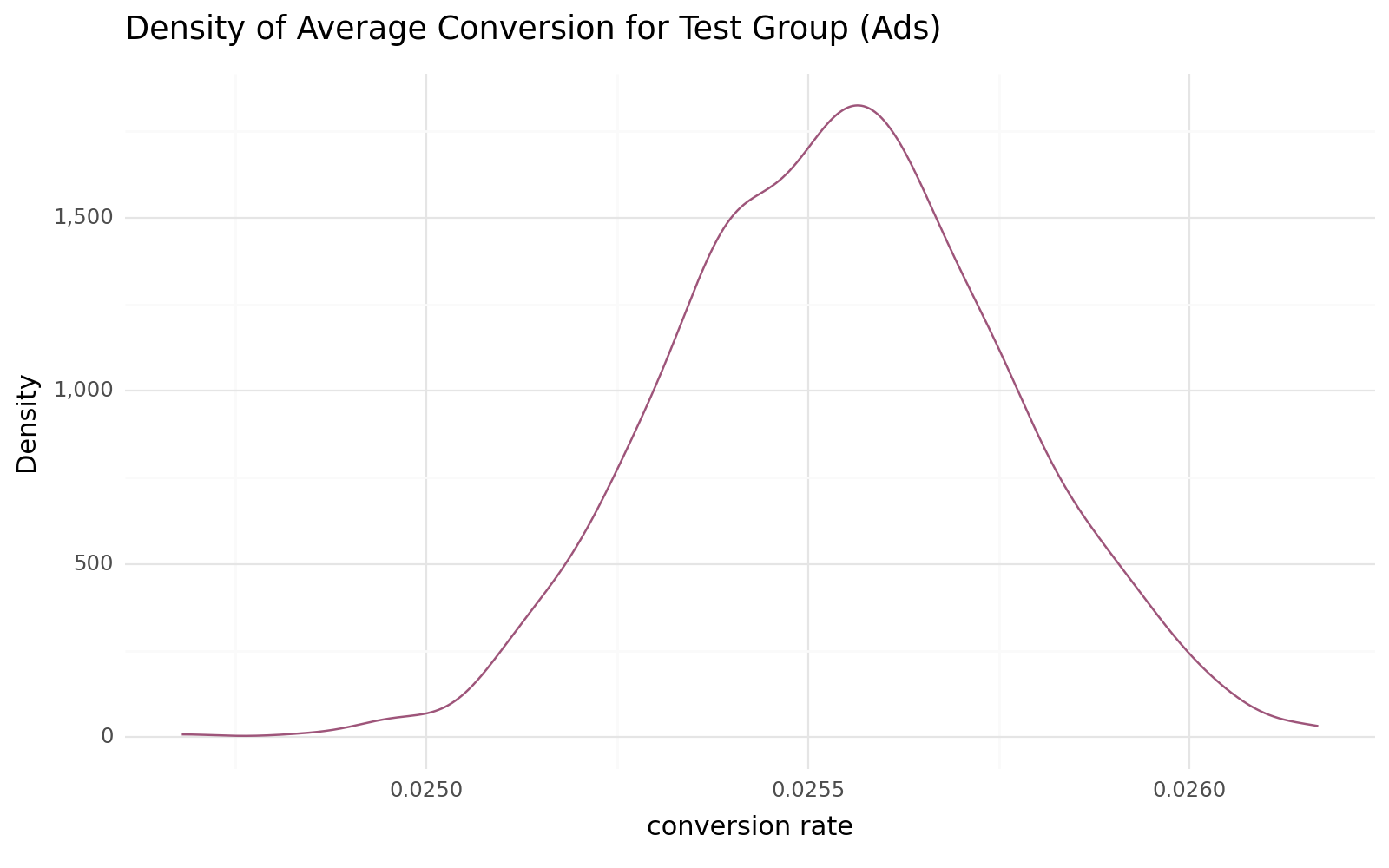
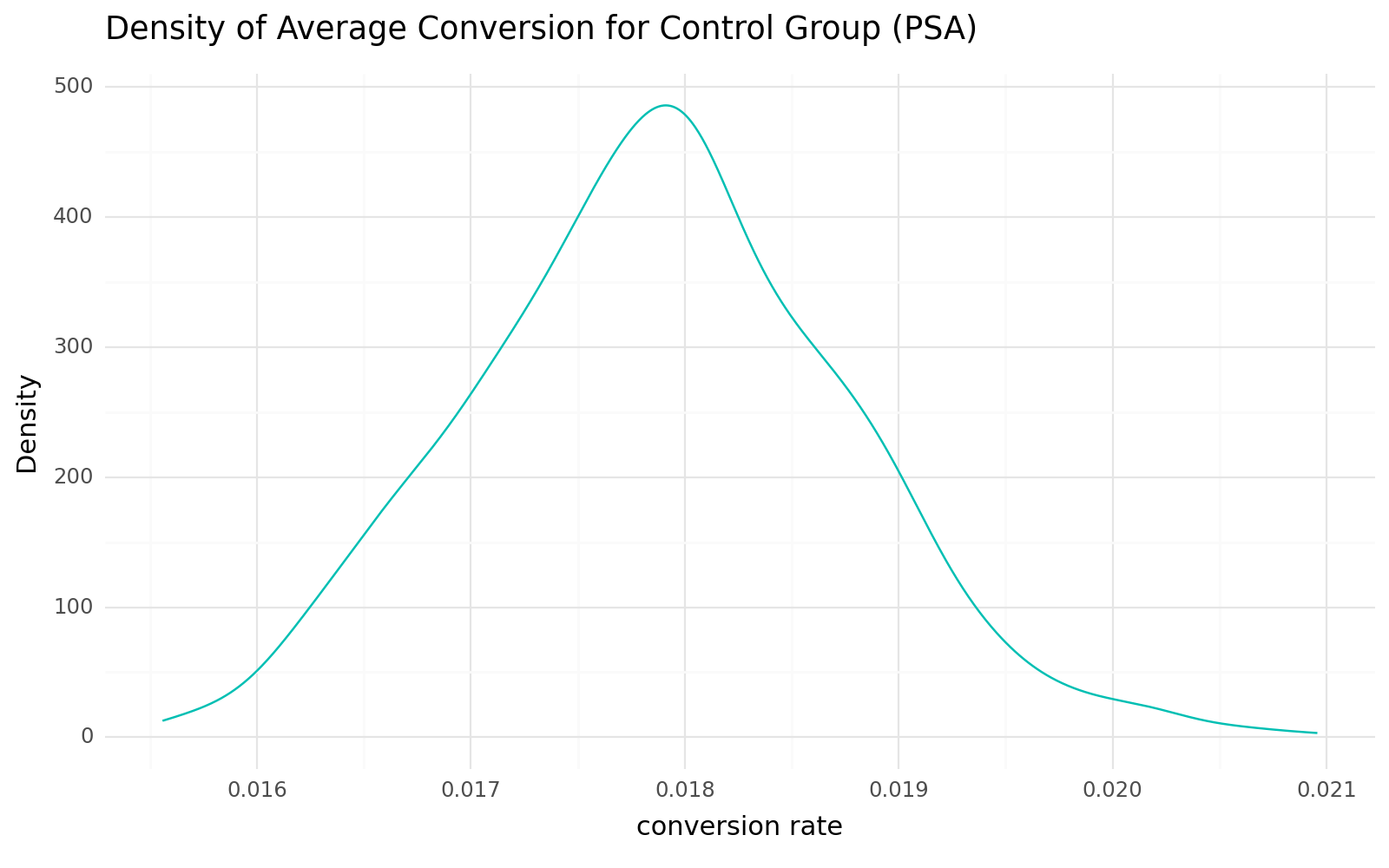
After a thorough exploration and summary of the performance metrics of both groups on the metrics page, we will leverage these insights to conduct the necessary tests. This will enable us to comprehensively assess the significance of these insights in relation to the conversion rates of both groups.
The null hypothesis is a statement that suggests there is no significant difference or effect caused by the change being tested.
The conversion rate of the `Test Group (Ads)` is equal to or less than the conversion rate of the `Control Group (PSA)`.
Symbolically, it can be expressed as H0: Conversion rate of Group A = Conversion rate of Group B.
Alternative Hypothesis: (Ha)
The alternative hypothesis proposes that there is a statistically significant difference or effect resulting from the change being tested.
The conversion rate of the `Test Group (Ads)` is significantly greater that the conversion rate of the `Control Group (PSA)`.
Symbolically, it can be expressed as Ha: Conversion rate of Group A > Conversion rate of Group B.
Conversion Rate
Mean: 0.026
Standard Deviation: 0.158
Mean: 0.018
Standard Deviation: 0.132
Following the strategic shift from a long-standing Public Service Announcement (PSA) to a new advertising campaign, After conducted an analysis of the impact on conversion. In the A (test) group, consisting of users exposed to the ads, we observed an encouraging average conversion rate of 0.026, accompanied by a standard deviation of 0.158. This group's response showcases the potential of our new approach.
Meanwhile, the B (control) group, comprising users who continued to view the PSA, exhibited an average conversion of 0.018, with a standard deviation of 0.132.
These insights clarify the distinct performance of both groups, emphasizing the significance of the company's strategic shift in the pursuit of heightened sales. Analyzing these results, it's clear that the company's advertising efforts have set them on a path toward greater success and engagement with their user base.
Sample (Bootstrap)
Evidently, there is a substantial disparity in the sample size between the group exposed to the advertisement see metric page, comprising
96% of the total, and the group that viewed the PSA, which consitutes a mere 4%. When there is such an imbalance in sample size between experimental and control groups, it can potentially introduce several statistical analysis challenges.
These imbalanced sample sizes can impact the statistical power of the analysis and the precision of the estimates. Specifically, the group with the larger sample size is likely to yield more precise estimates compared to the group with the smaller sample size. Therefore, in this scenario, it becomes crucial to consider strategies with approprate statistical techniques capable of addressing imbalanced sample size, including weighted analysis or resampling methods like bootstrapping.
Following the creation of numerous bootstrap samples and subsequent calculation of average conversion rates for both the test and control groups, an examination of the depicted distributions and density plots reveals a characteristic bell curve pattern, strongly suggesting a normal distribution.
To further validate the normality assumption of our samples, a Shapiro-Wilk test was conducted. This test is employed to assess whether the test and control conversion samples adheres to a normal distribution. In this context, the null hypothesis posits that the data follows a normal distribution, while the alternative hypothesis suggests otherwise.
The results of the test yielded p-values of 0.38 for the test group and 0.84 for the control group samples, both of which surpass the significance level of 0.05. Consequently, we retain the null hypothesis, signifying that the sampled distributions exhibit normality.
This affirmation allows us to confidently apply statistical tests, as they rely on the fundamental assumption of normality.
T-test
The T-statistic of approximately 268.854 which serves as indicator of the magnitude of the difference between the test and control groups is high enough, indicating a subtantial difference between the groups. While the P-value which is < 0.05 (significate level), is exceptionally low small, signifying an extremely low likelihood of observing this level of difference by random chance alone.
Evaluation
Since the p-value is significantly less than the chosen significance level (0.05), the null hypothesis is decisively rejected.
This provides strong evidence in favor of the alternative hypothesis, indicating that there is a statistically significant difference between the test group and the control group being compared.
To summarize this, the t-test results reveal a statistically significant difference between the test (users with Ads views) and control group (users with PSA views), with the t-statistic and p-value pointing to a subtantial distinction.
This indicates that the advertisement has a significant impact on the conversion rate compared to the public service announcement.
Following the evaluation of the significance indicating a higher conversion rate for the ads, here are three key recommendations:
Optimize Ad Placement Strategy:
The analysis indicates that the advertisement significantly outperforms the PSA in terms of conversion rate. To maximize this advantage, the company should consider strategic placement of ads during peak user engagement periods, based on the insights gathered regarding daily and hourly views. By aligning ad exposure with when users are most active, the company can enhance the chances of conversions and improve ROI.
Segmentation for Targeted Marketing:
Identify user groups that responded exceptionally well to the ads and tailor marketing strategies specifically for them. Understanding the demographics and behaviors of these high-conversion groups can help refine the message and target, thus boosting conversion rates.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation:
While the analysis provides compelling evidence of the ads' positive impact, to maintain and build upon these gains, it's crucial for the company to implement continuous monitoring of user behavior and adapt marketing strategies accordingly. Stay agile in responding to changing trends, user preferences, and competition to ensure sustained growth in conversion rates.
By implementing these recommendations, success in the advertising efforts can be capitalized and proper foundation layed for ongoing improvements and enhanced conversion rates.